How to Convert IEC 60044-1 Standard Protection Classification to IEEE Standard Voltage Rating?
 |
| MiCom P63x Protection Relay |
There are a series of protection relays such as MiCom protection relays that are compatible with ANSI/IEEE CTs as specified in the IEEE C57.13 standard. The applicable class for protection is class "C", which specifies a non air-gapped core. The CT design is identical to IEC class P but the rating is specified differently.
The IEEE C class standard voltage rating required will be lower than an IEC knee-point voltage. This is because the IEEE voltage rating is defined in terms of useful output voltage at the terminals of the CT, whereas the IEC knee-point voltage includes the voltage drop across the internal resistance of the CT secondary winding added to the useful output. The IEC knee-point is also typically 5% higher than the IEEE knee-point.
Read: What are the Conditions in Selecting Current Transformer in Protective Relaying
Where IEEE standards are used to specify CTs, the C class voltage rating can be checked to determine the equivalent knee-point voltage (Vk) according to IEC.
The equivalence formula is:
Vk = (C x 1.05) + (Ksc x In x Rct)
Vk = (C x 1.05) + (100 x Rct)
Note: IEEE CTs are always 5A secondary rated, i.e. In =5A, and are defined with an accuracy limit factor of 20, i.e. Kssc =20.
Read: Types and Classes of Current Transformers According to IEC 60441
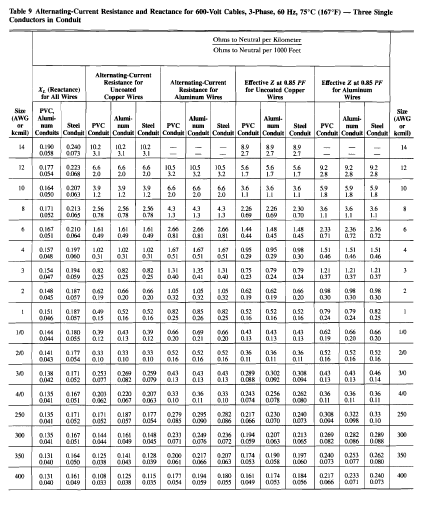
The following table allows C57.13 ratings to be converted to a typical IEC knee-point voltage:
- * Assuming 0.002 /turn typical secondary winding resistance for 5A CTs
- MiCom


.webp)








No comments: