What is the Importance of X/R Ratio?
What is X/R Ratio?
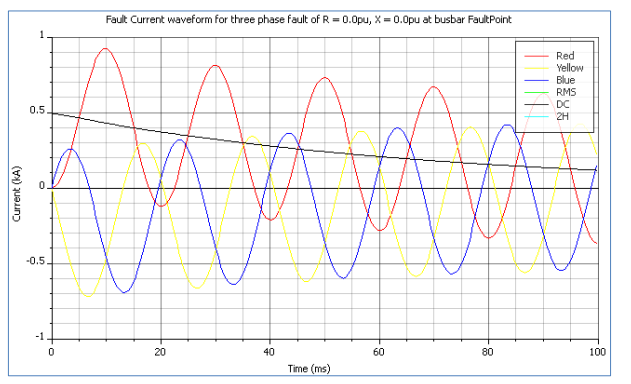
The X/R ratio is a measure of the ratio of the inductive reactance (X) to the resistance (R) of an electrical system. Knowing the X/R ratio is important for several reasons. Electrical Engineers need to know the importance of X/R ratio in doing fault calculations. This ratio can actually determine the peak asymmetrical fault current. Accordingly, the asymmetrical fault current can be way higher than the symmetrical fault current.
During a short circuit, the total current comprises two components:
- The AC component, which varies sinusoidally with time and is also known as the symmetrical current, and the DC component, which is non-periodic and decays exponentially with a time constant of L/R (where L/R is proportional to X/R).
- The DC component causes the symmetrical current to become asymmetrical. The X/R ratio impacts the magnitude of the DC component, which in turn affects the total current.
The Importance of X/R Ratio
A mismatch between the X/R ratio and the protective device can result in improper functioning of the protective device, leading to damage to the equipment or safety hazards to personnel. Secondly, it helps to optimize the electrical system's performance. The X/R ratio affects the voltage drop in the system and the transient response to switching events, such as motor starting or capacitor switching. A proper understanding of the X/R ratio can help in designing the electrical system to operate efficiently under various operating conditions. Thirdly, it helps in troubleshooting the electrical system. An X/R ratio that is too high or too low can indicate problems such as equipment malfunctions or incorrect wiring, which can be corrected to ensure the system is operating optimally.
It is important to note that the dc component of the fault current decays rather rapidly, reaching an insignificant value in a matter of 3 to 5 cycles of the power frequency. In this process, the rate of decay is determined by the X/R ratio of the circuit at the point of fault. That means, if the value of the ratio is higher then the DC component decay is slower which prolongs the danger as a result of the fault.
See: Protection Relays in Power System
X/R Ratio in Fault Current Calculation
X/R Ratio in Selecting Protective Device
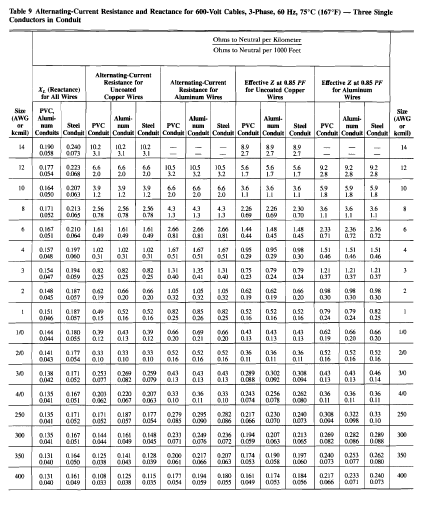
To select the appropriate protective device for a given system, it is essential to determine the X/R ratio of the circuit where the device will be installed. A protective device must have a suitable interrupting capacity that can handle the maximum short-circuit current that can occur in the circuit. The interrupting capacity of a protective device is typically specified in terms of its current rating and its withstand capacity.
The X/R ratio affects the magnitude and duration of the short-circuit current, which, in turn, affects the interrupting capacity required for a protective device. A circuit with a high X/R ratio will have a longer duration of the fault current, and therefore, requires a protective device with a higher interrupting capacity. Conversely, a circuit with a low X/R ratio will have a shorter duration of the fault current, and a protective device with a lower interrupting capacity may be sufficient.
Furthermore, the X/R ratio can also affect the operation of the protective device. For example, a protective device designed for use in a high X/R ratio circuit may have a longer time delay before tripping to account for the longer duration of the fault current. In contrast, a protective device designed for use in a low X/R ratio circuit may have a shorter time delay to account for the shorter duration of the fault current.
In conclusion, the X/R ratio is a critical parameter in electrical power systems that affects the behavior of circuits and components. Its importance lies in its impact on fault calculations, protective device selection, equipment design, power system stability, and fault detection. Knowledge of the X/R ratio is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems, and proper selection of protective devices that can handle the maximum short-circuit current that can occur in the circuit.
~ End

.webp)









¿How is the X/R ratio calculated with simulation software (E.G. Digsilent)?
ReplyDeleteProtection of Information: No Retail Electric Provider can deliver any client explicit data to another Retail Electric Provider or some other organizations without your authorization.
ReplyDeletehigh voltage diode manufacturer
Exchanging and estimating voltage sources with high inner impedance is dependent upon mistakes like balance flows, stray spillage ways, and electrostatic obstruction. Shunt capacitance may expand the settling time. China mosfet manufacturer
ReplyDelete