What are the General Guidelines in Electrical Design?
 |
| Electrical Design |
To get the best results, an electrical engineer needs to be aware of specific guidelines so that they can identify the required information that needs to be included.
Determine the load power demands
Electrical design starts with the study of the nature of the proposed project in relation to the understanding of all codes, legislations, and standards. The total power demand can be calculated from the data relative to the location and power of each load, together with the knowledge of the operating modes such as the following:
- steady state demand
- starting conditions
- non-simultaneous operation
Read: How To Prepare Schedule of Loads
Service connection
Depending on the necessity and the size of the electrical installation, it is better to select properly the service locations.
- Medium Voltage Level Service Connections - A consumer-type substation will then have to be studied, built and equipped. This substation may be an outdoor or indoor installation conforming to relevant standards and regulations (the low-voltage section may be studied separately if necessary). Metering at medium-voltage or low-voltage is possible in this case.
- Low Voltage level Service Connections- The installation will be connected to the local power network and will (necessarily) be metered according to LV tariffs.
Architecture of the Electrical Distribution
The whole installation distribution network needs to be considered as a complete system. With respect to the necessity of the project, a selection guide is proposed for determination of the most suitable architecture. MV/LV main distribution and LV power distribution levels are covered. Neutral earthing arrangements are chosen according to local regulations, constraints related to the power-supply, and to the type of loads.
The distribution equipment such as switchgears, panels, MSS and other equipment must be determined from building plans and from the location and grouping of loads. The type of premises and allocation can influence their immunity to external disturbances.
Protection against electric shocks
The earthing system (TT, IT or TN) having been previously determined, then the appropriate protective devices must be implemented in order to achieve protection against hazards of direct or indirect contact.
Read: Basic Safety Provision for Electrical Installation According to BS 7671
Sizing and Protection
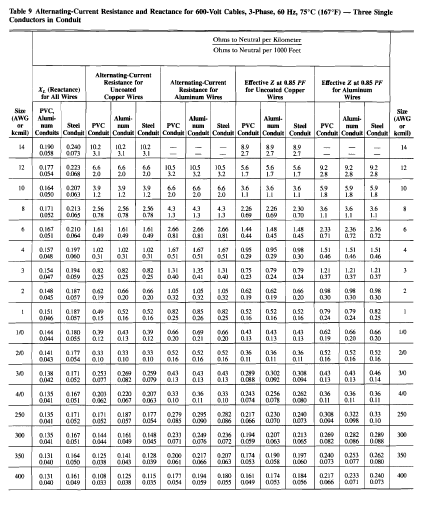
Every part of the electric circuit must undergo a detailed study. It starts from the calculation of the rated currents of the loads, the magnitude of short-circuit currents, and the type of protective devices, the sizes of circuit conductors, and the specification of the cable ducts and conduits. Also, anything that can affect the rating of the conductors must also be identified.
- The voltage drop complies with the relevant standard
- Motor starting is satisfactory
- Protection against electric shock is assured
- The possible temperature where the electrical system is to be installed
- Earth Fault Loop
Read:
The performance required by the switchgear will determine its type and characteristics. The use of cascading techniques and the discriminative operation of fuses and tripping of circuit breakers are examined.
Protection against overvoltages
Direct or indirect lightning strokes can damage electrical equipment at a distance of several kilometers. Operating voltage surges, transient and industrial frequency over-voltage can also produce the same consequences. The effects are examined and solutions are proposed.
Energy efficiency in electrical distribution
Implementation of measuring devices with an adequate communication system within the electrical installation can produce high benefits for the user or owner: reduced power consumption, reduced cost of energy, better use of electrical equipment
Reactive energy
The power factor correction within electrical installations is carried out locally, globally or as a combination of both methods.
Harmonics
Harmonics in the network affect the quality of energy and are at the origin of many disturbances as overloads, vibrations, ageing of equipment, trouble of sensitive equipment, of local area networks, telephone networks. This chapter deals with the origins and the effects of harmonics and explain how to measure them and present the solutions.
Particular supply sources and loads
Particular items or equipment are studied: b Specific sources such as alternators or inverters b Specific loads with special characteristics, such as induction motors, lighting circuits or LV/LV transformers b Specific systems, such as direct-current networks.
Reference:
- Schneider Electric

.webp)








It??s nice to definitely locate a blog the spot that the blogger is . Appreciation for making your blog site. electrical contractors in biloxi
ReplyDeleteExcellent to be visiting your blog again, it has been months for me. Rightly, this article that I've been served for therefore long. I want this article to finish my assignment within the faculty, and it has the same topic together with your article. Thanks for the ton of valuable help, nice share. gta general contractors
ReplyDeleteReally such a very informative blog. We are looking for wholesale electrical wire I Hope we can get the best deal out there.
ReplyDeleteThe information which you have provided is very good and essential for everyone. If you're looking for wholesale electrical wire. I recommend amwire you can visit their website.
ReplyDelete"Innovation drives the battery industry forward." standard battery packs
ReplyDeleteVery useful for cutting foam for packaging. hot wire foam cutter
ReplyDeleteEvery piece of Zolytech equipment undergoes rigorous quality checks to ensure it meets international standards for safety, performance, and durability. zolytech.ru
ReplyDelete