Substation Control System
 |
| Photo Credit: Windpower Engineering and Development |
Due to our earnest desire to reduce carbon footprints, the utilization of renewable energy is no longer an option but a necessity. However, the use of these alternative sources of energy such as solar and wind power, in particular, can develop a serious problem for the grid when its penetration is already at a high level. The technical issue emanates from the inherent variability of these alternative sources of energy.
Unlike thermal power sources that we normally utilized for baseload plants, solar and wind power can disappear anytime while it is operating and the sudden power drop can create instability to the power grid.
Related Article: IEC 61850 Logical Nodes and Data Classes in Power System Automation Data Modelling
For this reason, automating the power grid is also necessary following the massive penetration of these alternative sources of energy. Before applying the whole context of power system automation, it is necessary that substations are the ones that need to be automated first. This is because the substation serves as the core junction between the power producer and the consumers. In this regard, the speed and reliability of data transmission can be realized.
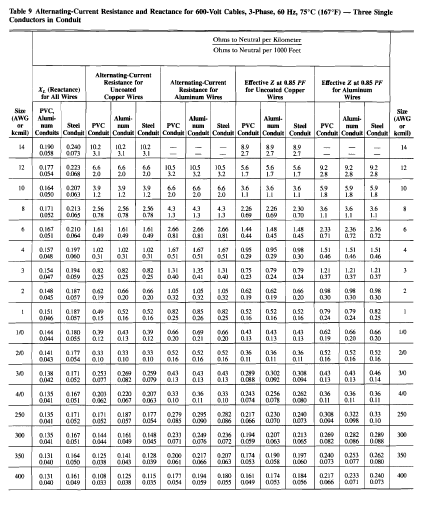
The basic configuration of the substation control system is shown in the figure below. In this diagram, we can see its main components such as:
- Bay Control Unit - is used to act as the link between the switchgear (devices) and the control center for monitoring and controlling.
- Data Acquisition Controller (SCADA) - a software package that is positioned on top of hardware to which it is interfaced, in general via programmable logic controllers (PLCs), or other commercial hardware modules.
- Human Machine Interface - the interface where the human operator can interact with the system and perform specific actions.
- GPS Antenna and Receiver - used for time synchronization.
- Instrument Transformers - instruments used to collect electrical data such as voltage and current.
- Local Area Network Device - used to interconnect different components in the system.
These devices are integrated in order to deliver important functions such as:
- Trending - collects remote field data and plots the data points into an advanced charting system to show secondly reports, hourly reports, daily reports, and more.
- Alarm Handling - SCADA alarm is one of the main tools to ensure safe and manageable system operation.
- Logging/ Archiving - Logging/ archiving is storing of data based on past events.
- Report Generation – SCADA can generate reports based on client requirements.
- Controlling - control the operation of switches, relays, and protection devices.


.webp)










No comments: